Blog•Mar 6, 2026
Kvantify Completes 2nd Close of €7M Round to Advance Quantum Drug Discovery
Kvantify announced the second close of its €7 million funding round, with the European Innovation Council Fund and Denmark’s Delphinus Venture Capital as lead investors. The capital will support the rollout of its Qrunch platform, which runs quantum chemistry workloads on existing quantum hardware, and broaden partnerships with drug‑discovery firms. Launched in November 2025, Qrunch aims to deliver realistic molecular simulations that classical computers struggle with. The infusion positions Kvantify to accelerate its roadmap and strengthen Europe’s quantum‑driven life‑science ecosystem.
By HPCwire

Blog•Mar 5, 2026
Quantum-Safe Security: What CISOs Need to Know Now (Before It’s Too Late)
Quantum computing threatens to break today’s asymmetric encryption, making current data protection obsolete. The most immediate risk is a “harvest now, decrypt later” attack, where adversaries steal data today and decrypt it once quantum capabilities mature. Experts estimate viable quantum...
By Erdal Ozkaya’s Cybersecurity Blog

Blog•Mar 5, 2026
Next Gen Spotlights: Preparing for a Post-Quantum World – Q&A with Cavero Quantum
Cavero Quantum, a University of Leeds spin‑out, has developed post‑quantum cryptography and password‑less authentication that can run on ultra‑constrained devices such as SIM cards. Backed by the UK government’s CyberASAP programme, the startup moved from a funded demo to real‑world...
By IT Security Guru

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Xanadu Highlights Path to Public Listing, Scalable Quantum Computing
Xanadu Quantum Technologies announced its plan to go public via a business combination with Crane Harbor Acquisition Corp, valuing the company at roughly $3.1 billion and leaving it with about $455 million in net cash. The firm showcased Aurora, its first networked,...
By Quantum Zeitgeist
Blog•Mar 4, 2026
MicroCloud Hologram Advances Deployable Quantum Recurrent Neural Network Technology
MicroCloud Hologram Inc. (HOLO) announced a Quantum Recurrent Neural Network (QRNN) built around a novel Quantum Recurrent Block (QRB) architecture designed for noisy intermediate‑scale quantum (NISQ) devices. The QRB acts as a modular, repeatable subcircuit that drastically reduces coherent‑time consumption,...
By Quantum Zeitgeist

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
DOE Advances Domestic Capabilities for Producing Quantum Materials
The Department of Energy announced that Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has built systems to turn commercially sourced isotopically enriched silicon and germanium into high‑purity silane (SiH₄) and germane (GeH₄) gases. These precursor gases are essential for quantum information science and...
By HPCwire

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Quantum Elements Reports Record Logical Qubit Fidelity in Nature Communications Study
Quantum Elements, together with USC, IBM and RWTH Aachen, published a Nature Communications paper showing the highest‑fidelity entangled logical qubits on a 127‑qubit superconducting processor. By merging quantum error detection with a novel logical dynamical decoupling (LDD) technique, the team...
By HPCwire
Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Keyfactor Advances Automation for Modern Digital Trust Environments
Keyfactor unveiled a suite of automation tools that modernize public key infrastructure, certificate lifecycle management, and digital signing. The enhancements address shrinking TLS certificate lifespans, tighter compliance mandates, and the emerging threat of quantum‑computing attacks. New hybrid cryptographic models let...
By Quantum Zeitgeist
Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Origin Quantum Computing Achieves High-Accuracy Flux Crosstalk Compensation in Superconducting Qubits
Origin Quantum Computing, in partnership with USTC, unveiled a spin‑echo‑based method that separates quantum and magnetic flux crosstalk in superconducting qubits. The technique, combined with a learning‑driven high‑parallelism measurement scheme, stabilizes frequency‑shift fluctuations to a 20 kHz noise floor. After compensation,...
By Quantum Zeitgeist

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Fireside Chat with dMY Squared Technology Chairman, Horizon Quantum CEO & CFO, Mar 9 at 1:15PM ET
IPO Edge will host a 45‑minute fireside chat on March 9 featuring dMY Squared Technology Chairman Harry You and Horizon Quantum CEO Dr. Joe Fitzsimons. The session will detail the recently completed business combination that makes Horizon Quantum the first publicly...
By IPO Edge
Blog•Mar 4, 2026
University of Toronto Centre Awards Bell Prize for Neutral Atom Research
The University of Toronto’s Centre for Quantum Information and Quantum Control awarded the ninth John Stewart Bell Prize to Mikhail D. Lukin, Antoine Browaeys, and Mark Saffman for pioneering neutral‑atom quantum computing. Their work demonstrated reconfigurable optical‑tweezer arrays that can...
By Quantum Zeitgeist

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Thales Validates Post-Quantum Cryptography on Live Networks, Enabling Ongoing Protection
Thales demonstrated live‑network post‑quantum cryptography for 5G, remotely updating SIM and eSIM cards with quantum‑safe algorithms. The "crypto agility" approach eliminates the need for massive hardware swaps, enabling instant security upgrades across existing devices. The trial underscores Thales’ role in...
By Quantum Zeitgeist
Blog•Mar 4, 2026
NQCC SparQ Access Programme Supports Academic Research with Quantum Resources
The National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC) has launched the SparQ Access programme, granting UK academia access to more than 20 quantum computing platforms, including Azure Quantum, Rigetti, IonQ, IBM Quantum and various simulators. Applications for the May‑July 2026 window are...
By Quantum Zeitgeist

Blog•Mar 4, 2026
Three or More Parties Now Securely Share Encryption Keys Via Quantum Links
Researchers from the University of York propose a holistic framework for multiparty quantum key agreement (MQKA) that classifies protocols along three axes—network architecture, quantum resources, and security model. By mapping existing schemes onto this design space, they demonstrate error‑rate reductions...
By Quantum Zeitgeist

Blog•Mar 3, 2026
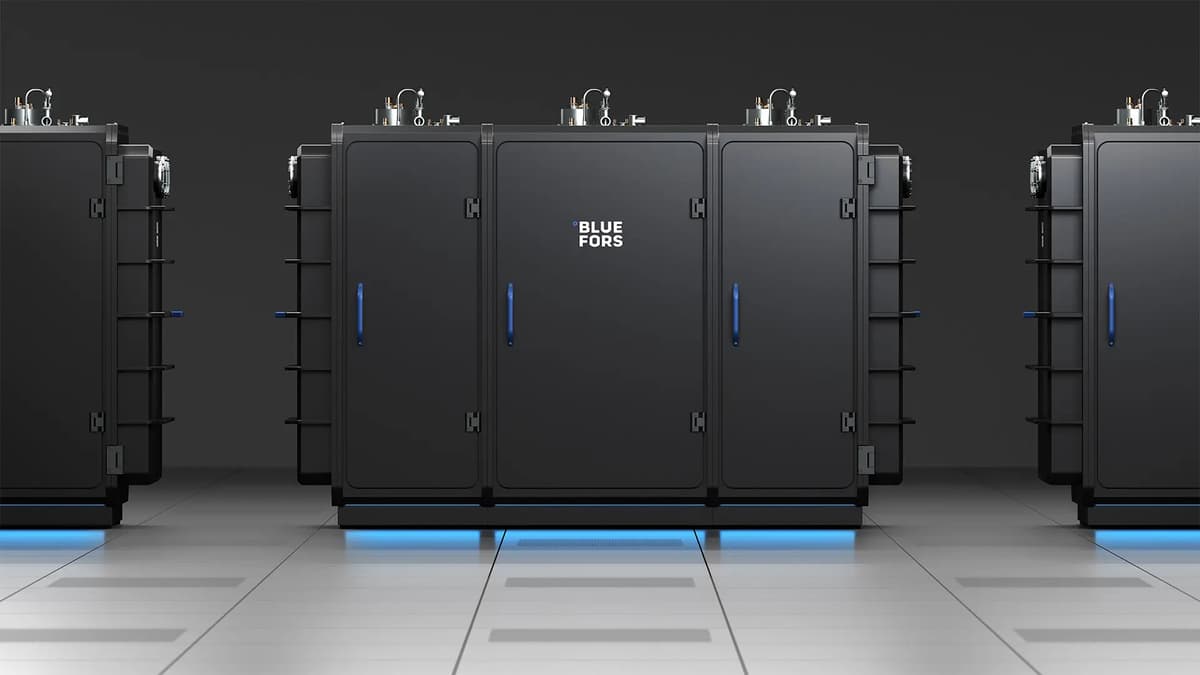
Bluefors Introduces Expandable Platform Supporting High Qubit Count Quantum Hardware
Bluefors unveiled its Modular Cryogenic Platform, an expandable vacuum‑chamber system designed to meet the scaling demands of quantum computers. The architecture lets users add modules incrementally, increasing cooling capacity and qubit density without replacing the entire infrastructure. Each module supports...
By Quantum Zeitgeist